JUNIOR SECONDARY AGRICULTURE & NUTRITION REVISION
GRADE 7 AGRICULTURE & NUTRITION
What is soil pollution? (1mk)
- Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil with harmful substances.
State the two names that are used to refer to the harmful substances that causes soil pollution. (2mks)
- Soil contaminants.
- Soil pollutants.
Grade 7 learners
were discussing various causes of soil pollution. List down any four causes
they might have discussed. (4mks)
- Excessive use of artificial fertilizers.
- Excessive use of agrochemicals.
- Poor disposal of plastic wastes.
- Poor disposal of chemical containers.
Mwalimu Julius
teaches Agriculture & nutrition in Kajiado junior secondary school. He
decided to ask his learners two examples of agrochemicals that might cause soil
pollution. Give the answers the learners might have given out.
(2mks)
- Pesticides.
- Herbicides.
Jeremy decided to ask mwalimu Julius ways that can be used in controlling pests and weeds to avoid soil pollution by the agrochemicals above when in farming. Suggest the methods
mwalimu Julius
gave out in response to Jeremy’s question. (3mks)
- Weeding by uprooting weeds to avoid herbicides.ü Weeding by uprooting weeds to avoid herbicides.
- Weeding by slashing weeds.
- Controlling pests by use of natural or organic pesticides such as ash, rabbit urine, Mexican marigold, pepper, rosemary plant extracts like garlic, neem oil etc.
- Control pest by planting various crop species.
Differentiate
between pesticides and herbicides. (2mks)
- Pesticides – these are agrochemicals used to control crop pests in the farm.
- Herbicides – these are agrochemicals that are used to control weeds in the farm.
Grade 7 learners came across the following as causes of soil pollution. Describe how each causes soil pollution. (4mks)
a.) Excessive use of artificial fertilizers.
b.) Excessive use of agrochemicals.
c.) Dumping plastic wastes in the farm.
d.) Poor disposal of Chemical containers.
- Excessive use of artificial fertilizers – fertilizers usually introduce pollutants such as Nitrogen compounds and heavy metals which accumulate in the soil to toxic levels and become harmful to crops and soil living microorganisms.
- Excessive use of agrochemical – agrochemicals such as pesticides and herbicides become pollutants when they get into the soil, accumulate into the soil and become toxic to soil living microorganisms.
- Dumping plastic materials in the garden –plastic waste materials such as bottles do not decompose, they accumulate and contaminate the soil interfering with the growing crops or reduces agricultural land.
- Dumping chemical containers in the garden – chemical leftovers from chemical containers get into the soil, become pollutants by accumulating to toxic levels and become harmful to the soil living organisms.
- Surface run-off carrying contaminated water –surface runoff that contains any contaminants deposits them to the soil when passing over.
- Industrial wastes – waste from industries have dangerous chemical and heavy metals if not disposed off well it ends up into the soil which directly affects microorganisms.
What are soil contaminants? (1mk)
ü Soil contaminants are harmful substances that pollutes the soil. They are also called soil pollutants.
You have been
asked to state five safe soil pollution control practices. Give the answers you
will give out.
(5mks)
- Using the correct type and amount of artificial fertilisers.
- Use correct type and amount of agrochemicals.
- Safe disposal of household waste water.
- Safe disposal of plastic wastes, containers, straws, bottles and containers.
- Safe disposal of used agricultural chemical containers.
- Practice organic farming. Organic farming refers to farming without use of agrochemicals.
- Reusing of plastic materials such as using bottles for drip irrigation.
- Recycling waste materials into other useful products.
- Planting trees and cover crops to reduce surface run-off than carry contaminants and distribute over the soil surface.
Students from Horizon school wanted to sensitize the community around the school on the dangers of soil pollution and the safe farming methods that can be used to prevent soil pollution. Identify four methods they can use to do so. (4mks)
- Dramatization.
- Presenting songs.
- Use of poems.
- Displaying posters.
Grade 7 learners visited a nearby farm and discovered that the soil was polluted. Write down four soil contaminants they might have found. (4mks)
- Artificial fertilizer.
- Agrochemical such as pesticides and herbicides.
- Plastic materials.
- Chemical containers.
How can we make the members of the community aware of soil pollution control measures? (2mks)
- Creating awareness message that is designed to educate the public on a wide range of farming practices that cause soil pollution and the control measures.
What is the importance of controlling soil pollution in farming? (2mks)
- ü Enables production of safe and healthy crops.
- ü Maintains soil productivity.
Your school has allowed grade 7 learners to visit the community around with awareness message on soil pollution and its control. State any materials you will use for this exercise.
- Posters.
- Manilla papers.
- Printed T-shirts.
- Public address systems etc.
Define the term water conservation measures. (2mks)
- These are activities done to prevent lose of water or to ensure water is retained or not wasted during its use or from different sources.
What is surface runoff? (2mks)
- Water that runs/flows on the ground surface during and after rainfall.
State any four damages caused by surface run off. (4mks)
- Cause soil erosion.
- Deposits contaminants such as fertilizer, oil, pesticides and dirt into water bodies causing both soil and water pollution.
- Destruction to crops.
- Causes damage to infrastructure such as roads, buildings etc.
You have noticed
that at home there is a lot of damage caused by surface runoff during and after
rainfall. Give two methods you will use to control the situation. (2mks)
- Constructing water harvesting structures.
- Use vegetative waterways to direct water to non-farming land.
State the
activities that increase the rate of soil erosion. (5mks)
- Overgrazing.
- Cultivation along steep slopes.
- Deforestation. (Cutting down of trees.)
- Human activities such as mining and quarrying.
- Animal trampling.
- Burning of vegetation.
- Removal of vegetation cover.
Give 5 reasons for conserving surface run off. (5mks)
- To conserve excess water and use during water shortage or scarcity.
- To reduce cost of farming. Money is not spent on water because it is available through conservation.
- To avoid water wastage.
- To avoid damage cause by surface run off.
- To make sure water is available throughout.
State the three methods used to conserve surface run-off. (3mks)
- Use of Water retention ditches.
- Use of Water retention pits.
- Use of earth basins.
- Dams.
What is a water retention ditch? (2mks)
- A trench constructed along the contours/across the slope to collect and hold surface run off when there is rainfall.


State the steps followed when constructing a water retention ditch. (4mks)
- Determine/identify contour lines using an A-frame.
- Mark contour lines with pegs.
- Dig soil along the marked lines to make a trench about 0.6m deep by 60cm wide.
- Remove the soil with a spade and throw it downward to form an embankment.
- Plant grass or any other crop on the embankment to help control soil erosion on the structure.
What is an earth basin? (2mks)
- An earth basin is a small pond or a depression that is constructed on the surface of land to collect surface run-off water after rains for use in farming.
Briefly describe the steps followed when constructing an earth basin. (4mks)
- Clear the area where the earth basin is to be constructed.
- Excavate the basin by digging the soil and throwing it to the sides to form an embankment.
- Leave the upper side of the basin open to allow the flow of run odd into the basin.
- Plant a crop or grass around the earth basin to prevent soil erosion.
What is a water retention pit? (2mks)
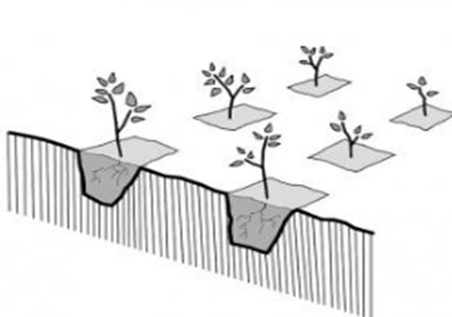
- This are small depression in which crops grow and are used to trap water around the base of the crop to be used by the crop. This reduces run-off.
Describe the steps followed when making a water retention pit. (3mks)
- Measure the spacing of the pits and mark with pegs.
- Dig the pits about 20-30 cm deep and spaced at 90 cm.
- The pits are planted with a crop. They help to hold surface run-off preventing soil erosion
The picture below shows a method used to conserve surface run-off.

a.) Name the structure shown. (1mk)
- Water retention pit.
b.) List down any four crops established in the structure shown above. (4mks)
- Banana suckers.
- Arrow roots.
- Napier grass.
- Sugarcane.
c.) Identify two other structures used to conserve surface run-off. (2mks)
- Water retention ditches.
- Earth basin.
Give three importance of water conservation in farming. (3mks)
- Surplus or excess water can be conserved and used during the times of water scarcity in the farm.
- Conserving water reduces the cost of farming. This is because money that would be used to buy water in the farm is saved.
- Conserving water ensures availability of water for human life and livestock.
- A lot of water is wasted during rainy season.
- Rain water which forms surface run-off after heavy downpour is prevented from damaging property.
Explain four problems facing water conservation in agricultural environment. (4mks)
- Lack of skills in water conservation due to lack of training.
- Negative attitude by members of the community due to lack of awareness on importance of water conservation.
- Water pollution from other human related activities such as use of excess fertilizer and agricultural chemicals.
List down four occasions/moments when vegetables lose nutrients. (4mks)
- During washing.
- When peeling.
- When cutting.
- During cooking.
Identify the practices to avoid when preparing vegetables to avoid loss of nutrients during the following.
a.) Washing. (4mks)
b.) Peeling. (2mks)
c.) Cutting. (2mks)
d.) Cooking time (1mk)
a.) Washing.
- Avoid soaking vegetables.
- Avoid washing vegetables for a long period of time.
- Avoid washing vegetables using warm water.
- Avoid cutting vegetables before washing.
b.) Peeling.
- Avoid over peeling or excessive vegetables.
c.) Cutting.
- Avoid cutting before washing.
- Do not cut vegetables thinly.
- Avoid exposing cut vegetables to air.
d.) Cooking time.
- Avoid overcooking vegetables.
- Cover vegetables during cooking time.
Grade seven learners of Kayole junior secondary were asked to list down benefits obtained from trees. State any five benefits. (5mks)
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Timber/poles.
- Firewood.
- Food for humans and animals.
- Income from selling products such as timber, fruits.
- Trees provide shade for both humans and animals.
- Trees provide organic matter that increase soil fertility.
- Trees conserve both water and soil.
Define the following. (3mks)
a.) Afforestation.
b.) Deforestation.
c.) Reforestation.
_________________________________________________________
a.) Afforestation – refers to planting trees where tress had never existed.
b.) Deforestation – indiscriminate removal of trees from forested areas
c.) reforestation – means planting of tress where forests have been cleared
State three roles of trees in soil and water conservation. (3mks)
- They protect the soil from raindrop erosion by reducing the force with which it fall on the ground.
- Trees provide shade hence reducing loss of moisture through evaporation.
- Trees act as windbreaks preventing wind erosion.
- Roots of trees binds the soil particles together.
- Trees also reduce speed of running water thus reducing its erosive power which reduces soil erosion.
- Tree leaves decay/decompose to supply humus to the soil which improves soil fertility and water infiltration.
Grade 7 learners
were asked by the school to present various ways of taking care of trees in the
environment. List any four they might have presented. (4mks)
- Watering trees.
- Fencing to protect against animal damage.
- Controlling pest and diseases.
- Pruning to remove damaged parts.
- Cause soil erosion.
- Damage crops.
- Causes damage to infrustracture such as roads, buildings , pipes and bridges.
- Deposits contaminants such as chemical fertilizers, oil and pesticides into water bodies causing water polution.
You can reach our customer
You can reach our customer
Surface run off is the water that flows on the ground surfaces during and after rainfall.
- Cause soil erosion.
- Damage crops.
- Causes damage to infrustracture such as roads, buildings , pipes and bridges.
- Deposits contaminants such as chemical fertilizers, oil and pesticides into water bodies causing water polution.
You can reach our customer
You can reach our customer
Surface run off is the water that flows on the ground surfaces during and after rainfall.
- Cause soil erosion.
- Damage crops.
- Causes damage to infrustracture such as roads, buildings , pipes and bridges.
- Deposits contaminants such as chemical fertilizers, oil and pesticides into water bodies causing water polution.
You can reach our customer
You can reach our customer